- 2020/12/30
- 28979
- 165
COVID-19 has thrown the world into a global recession and marked the beginning of the 0-Touch Economy. Whether the 0-Touch Technology or Services can bring about real economic benefits for the users or the market depends on whether the technological innovations and value-add can shorten the distance in terms of time and space between people or objects in the 0-Touch Economy. The Industry, Science & Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), of the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) has proposed a framework of four innovative models for the program “0-Touch Economy, 0-Distance Innovation,” to assist industries in the exploration of their own strengths and in the development of strategies appropriate to the current challenges. It is hoped that industries can transform from the crisis to opportunities after COVID-19 with the secret weapons of innovation with agility and focus and digital transformation.
0-Touch Economy requires 0-Distance Innovation
To curb the spread of COVID-19, governments around the world have banned travel, ordered lockdowns, and even implemented curfews. Whilst these measures controlled the pandemic to a certain degree, the restrictions on the mobility of billions of people have caused a shortage of labor and components at factories, disrupted the supply chain, and shrunk the sales of many industries, e.g. Consumer goods, automobiles, and pharmaceuticals. The loss of mobility and employment has also dampened spending and affected many service industries such as air traffic, overseas education, travel, entertainment, hotels, consumer goods and luxury goods. COVID-19 has brought the global economy to its knees, but it has also catalyzed the rise of the 0-Touch Economy. In the long run, the success of the 0-Touch Technology or services in creating substantive economic benefits for the users or the market depends on whether the technological innovations and value-add can effectively reduce the distance in terms of time and space between people or objects in the 0-Touch Economy.
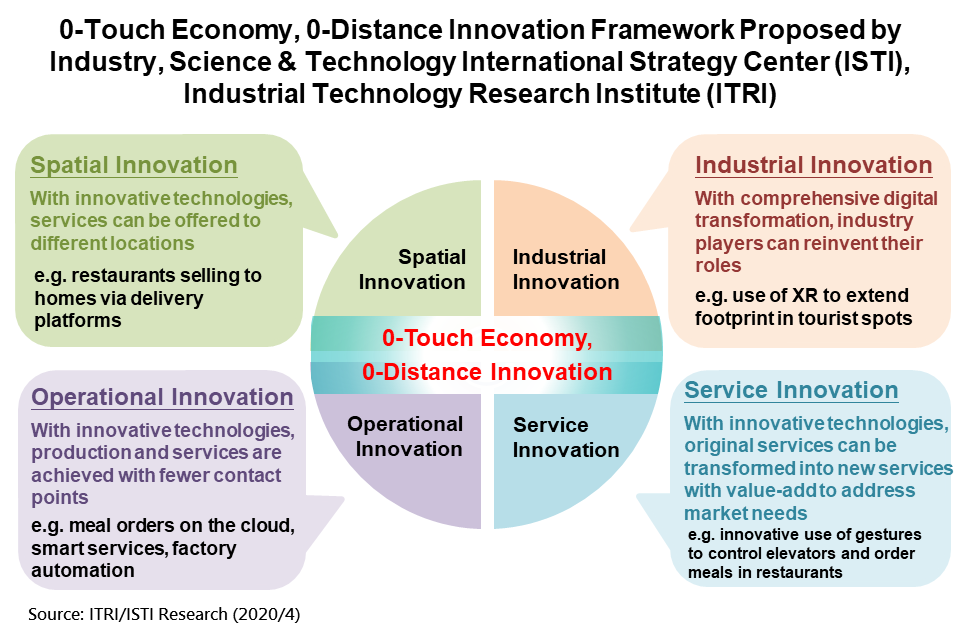
Four pillars of 0-Distance Innovation to accelerate industry transformation
ISTI of ITRI began, in March, to advocate the concept of HQ Economics to industries in Taiwan in their thinking regarding a new blueprint for global logistics. Smart resilient enterprises, empowered by digital transformation, will be able to respond to the impact of COVID-19 and the next adversity with better agility and recovery capabilities to mitigate the adverse effects of disasters. ISTI has followed this up with the innovation framework of “0-Touch Economy, 0-Distance Innovation” to create the secret weapons of innovation with agility and focus, and digital transformation, so that industries can transform the crisis into opportunities after COVID-19. The idea is to integrate digital technologies to provide an immersive experience and cross-industry business models to service remote users. Distance is shortened through cloud technology, and cross-domain experience and services are rendered with O2O (Online-to-Offline) integration.
Figure 1: 0-Touch Economy, 0-Distance Innovation Framework Proposed by Industry, Science & Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI)
0-Distance Innovation Model 1: Spatial Innovation
To control the spread of COVID-19, long-distance models such as remote working, remote medicare, food & beverage delivery, online gaming, and online education that were previously not considered mainstreamhave become the preferred choice. In the beginning, the public had to accept “spatial innovation” of the 0-Touch Economy to avoid the coronavirus. However, the sudden influx of a large number of users became a stress test on the system. Problems such as traffic bottlenecks, information security concerns, and poor user experience emerged. At this juncture, service providers rushed to adjust hardware/software architectures and service designs, so that online broadcasting or conferencing apps could be used by schools when face-to-face lecturing was not possible. This has replaced the traditional online teaching methods which were mostly based on non-real-time streaming and made remote learning widespread. This is the so-called “0-Distance Spatial innovation”.
0-Distance Innovation Model 2: Operational Innovation
Operational innovationsare the most familiar and most discussed. Smart automation, driverless vehicles and intelligent customer care services are set to replace humans. This also allows 0-touch and enables production and service offerings to continue during the pandemic. Previously, the high entry barriers and costs associated with smart factories, Industry 4.0, or intelligent customer care deterred small-and-medium enterprises. However, the development of smart machine boxes has enabled manufacturers to collect data and statistics of the production process, remotely monitor and operate the facilities, and communicate between workstations as part of smart manufacturing. On the cloud table-booking and ordering, and mobile payment ensures customers of a dining experience that is safer and more hygienic. This type of 0-Distance Operational Innovation needs a final push from the government in the form of emergency aid and industry policies, to accelerate immediate transformation during this crisis.
0-Distance Innovation Model 3: Service Innovation
To prevent the spread of the coronavirus, institutions and public venues are monitoring the body temperature of personnel and visitors. Whilst thermal image sensors are already a 0-touch application, their technical limitation means queuing for inspections is still necessary. Long lines during rush hours for students or vehicles has in fact increased the risk of infection. With support from the Department of Industrial Technology, of the Ministry of Economics Affairs and with the innovation and value-add from the project team, ITRI is transforming its infrared image sensing & detection technology previously intended for smart homecare for seniors, to thermal imaging technology for abnormal body temperature for the public and anti-virus applications. This technology will resolve the current pain point with applicability both indoors and outdoors; dynamic measurement of multiple persons; and easy and quick deployment. This 0-distance service Innovation will quickly be used to detect and prevent transmission of the COVID-19 virus and empower future innovation and applications.
0-Distance Innovation Model 4: Industrial Innovation
Among the biggest economic victims of the pandemic are tourism operators at beauty spots. By flexibly using the abovementioned 0-Distance Innovation strategy, the travel industry does not have to sit around in suffering. For example, operational innovation can be achieved with the introduction of smart customer care and digital marketing. The use of 360° panorama cameras or live streaming platforms can create “spatial innovation” by providing a sightseeing experience at tourist spots from a distance. The promotion of local specialty products via ecommerce platforms or tools can reach out to non-travelling consumers. This “service Innovation” can help to generate additional sales, maintain clientele through pre-booking, and maintain cash flows during the pandemic.
In fact, the conventional tourism operators in Taiwan are generally not resilient and have been challenged by the emergence of start-up travel companies and the rising popularity of independent travel driven by the shared economy. This is the perfect time for them to rethink their positioning and revise their business strategies. For instance, it is possible to establish digital sightseeing content by leveraging human capital and resources and applying VR (Virtual Reality), AR (augmented reality), CR (cinematic reality) to sites in the physical world. MR (mixed reality) can bring overseas tourist spots to Taiwan or even create new tourist sites. In this way, travel companies living off tourist spots can start to develop their own sightseeing destinations or theme parks. This allows for the reshaping of industry positioning and 0-Distance “industrial innovation.” It will create new revenue streams and enhance business resilience. The industry will be more prepared for when the next calamity or disaster hits and be able to reshape risks as opportunities.
IEKView
0-Touch Economy and 0-distance innovation is set to become the economic trend, innovation framework and a new lifestyle post COVID-19. These were in fact forecast to happen by the year 2030, by the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI), but the pandemic has just accelerated the process of application deployments and the arrival of new ways of living. In the context of the 0-Touch Economy and 0-distance innovation, the Industry, the ISTI would like to make the following suggestions to companies and industries in Taiwan:
- The 0-Touch Economy can only cash in by touching the heart of consumers with 0-distance innovations to shorten the distance between each other with mixed reality and present a full cross-domain experience and services.
- Companies should immediately embrace the 0-Touch Economy and 0-distance innovation via transformation, effective risk management and sustainable development with innovative technologies. This will strengthen the industrial competitiveness and survival resiliency of the companies.
- The era of 10x speed has arrived but there is no need to start from scratch on one’s own or to own every tool or asset relating to innovative technologies. Collaboration by utilizing existing resources has replaced solos and silos. Timeliness is always more important than perfection.
Finally, we would like to remind companies that human resources are their most important asset and core value. At this difficult time, companies should invest in these resources via training, rotation, and support programs to boost the key capabilities of employees in digital transformation. This will keep employees active and ready for action via training, support, and rotation schemes. In the reshuffling of industries amid the pandemic, the ingenuity of 0-distance innovations to empower the 0-Touch Economy will see successful upgrades and transformations. It will enhance corporate resilience so that companies can stay ahead of the fierce competition.